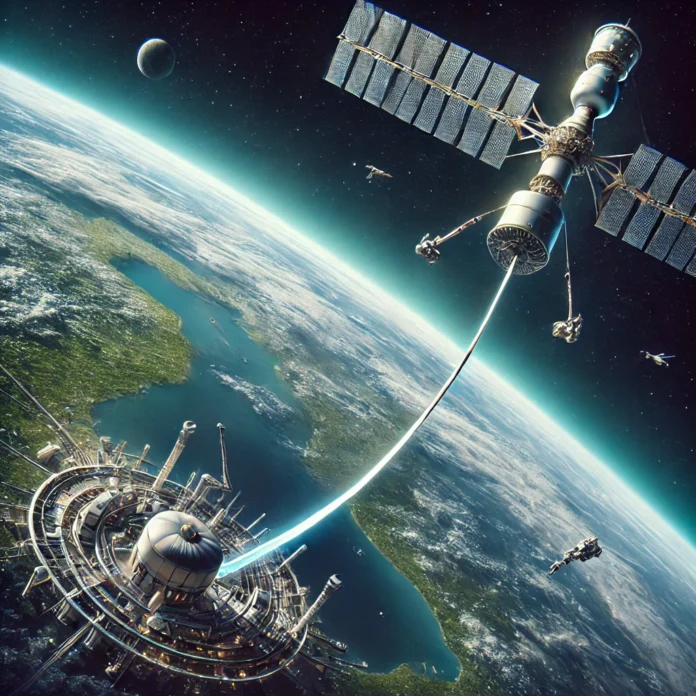
In the ever-evolving quest to make space more accessible and cost-effective, the concept of a space elevator stands out as one of the most revolutionary ideas. From its potential to drastically lower the cost of sending payloads into orbit to the technological innovations required to make it a reality, the space elevator represents the next frontier in space transportation.
The Cost Challenge of Traditional Space Launches
For decades, the cost of launching satellites and cargo into space has been a significant barrier to space exploration and commercialization. In 1985, launching a single kilogram to Low Earth Orbit (LEO) cost approximately $65,000, primarily due to the reliance on expendable rockets and the high cost of materials and fuel. By 2000, advancements in materials and engine designs had reduced this cost to $25,000 per kilogram, marking a significant step forward but still limiting frequent space missions.
The game-changing moment came in the 2010s, with the advent of reusable rockets like SpaceX’s Falcon 9. By 2020, the cost had plummeted to $2,720 per kilogram, and by 2024, SpaceX’s Falcon Heavy further reduced it to $1,500 per kilogram. These advancements are pushing space closer to being a more regular and economically viable frontier.
Forecasting Future Costs
Looking ahead, forecasts based on historical trends and technological advancements suggest that by 2050, the cost of launching a kilogram to LEO could drop below $500. However, when adjusted for present value using a 5% discount rate, this cost equates to around $161 in today’s terms, demonstrating the immense economic potential of continued innovation.
Enter the Space Elevator
The space elevator aims to further revolutionize space transportation. Unlike rockets, which require large amounts of fuel to escape Earth’s gravity, a space elevator would use a tether stretching from an equatorial base station on Earth to a counterweight in orbit. Robotic climbers would ascend and descend the tether, transporting cargo and passengers without the need for traditional rocket propulsion.
Technological Innovations Driving the Space Elevator
- Ultra-Strong Tether Materials
The core challenge is developing a tether strong and light enough to withstand immense tension. Current research focuses on carbon nanotubes and graphene, which could potentially meet these requirements. - Robotic Climbers
These climbers would rely on electric propulsion systems powered by laser beaming or solar energy to move up and down the tether efficiently. - Counterweight and Orbital Stability
A counterweight in geostationary orbit would keep the tether taut. This could be a satellite, space station, or even a captured asteroid.
Benefits of the Space Elevator
- Cost Efficiency: With potential costs as low as $100 per kilogram, a space elevator could outperform even the most advanced reusable rockets.
- Sustainability: Eliminating the need for rocket fuel reduces environmental impact.
- Continuous Access: Unlike rockets, space elevators could provide constant, reliable transport to orbit.
Challenges Ahead
Despite its promise, significant hurdles remain. The development of ultra-strong tether materials, mitigation of space debris risks, and the economic and political collaboration required for such a large-scale project are all critical factors that need resolution.
Conclusion: A Vision for the Future
As we project forward, the space elevator could redefine humanity’s relationship with space. By making space travel as routine and cost-effective as international shipping, it could unlock new opportunities for industries such as satellite communications, space tourism, and even the colonization of the Moon and Mars. With ongoing advancements in technology, the dream of building a space elevator is no longer science fiction—it is a challenge worth pursuing.
Author’s Note: The space elevator stands as a testament to human ingenuity and our unyielding desire to explore the cosmos. As we strive to overcome the challenges, it is only a matter of time before this futuristic vision becomes a reality. Stay tuned to Tecific for more updates on the latest advancements in space technology.